“Smart Factory solution integrates human capabilities and smart technologies to help accelerate and sustain performance improvement. It creates an organizational construct with a continuous improvement cycle, where people can continually upskill and leverage emerging technologies.”
4 building blocks for any smart factory, which make people and machines smarter:
Advantages of Smart Factory:

Smart Factory
Smart
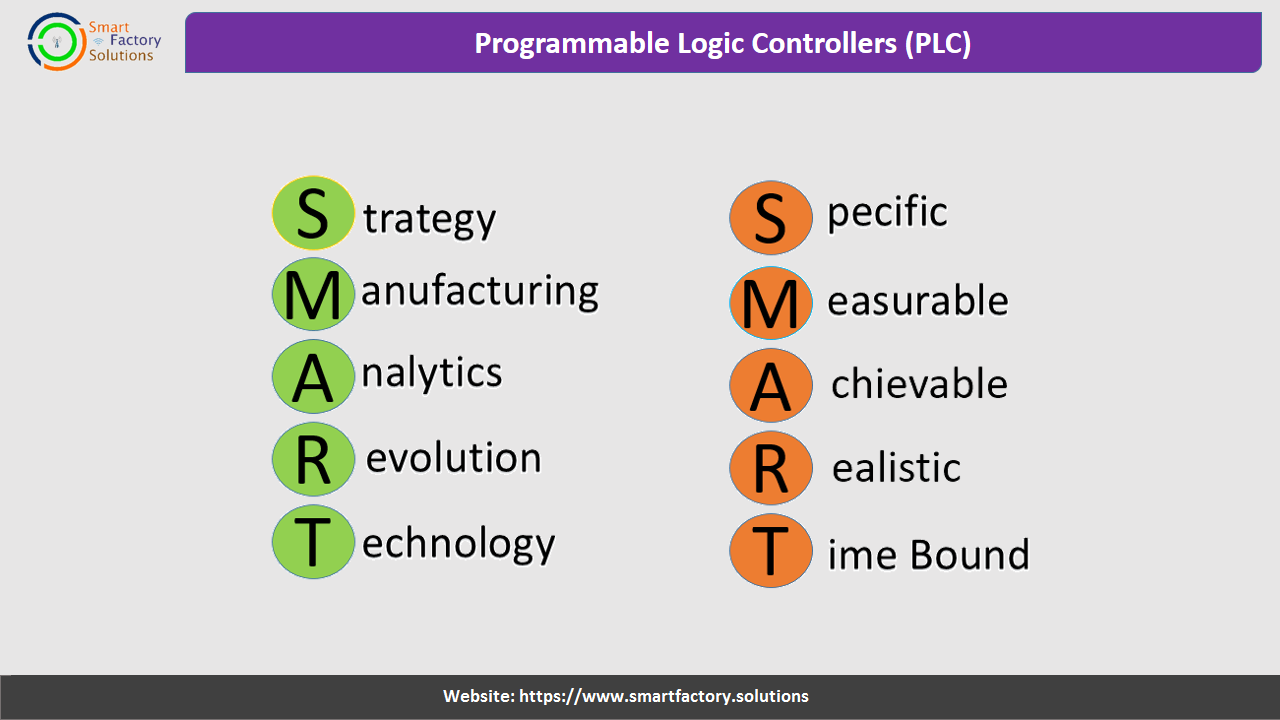
Specific goles are well defined and clear and what needs to be accomplished. What outcomes do you need to see in order to consider to goal accomplished.
Measurable goles enable you to evaluate wether or not the goal was achived or not . How you will decide wether the goal is completed or not.
Attainable and not impossible to achieve.
Realistic, and relevant to your life purpose.
Time Based goles into a specific timeframe and specify when they will be completed by.
Smart Factory is the vision of a production environment in which production facilities and logistics systems are organised without human intervention.
Industry 4.0 has been driving factories forward as the next industrial revolution promises to deliver a more responsive, adaptive and connected manufacturing line.
From the Internet of Things to Artificial Intelligence, there are plenty of innovative aspects to be considered when upgrading to a smart factory.
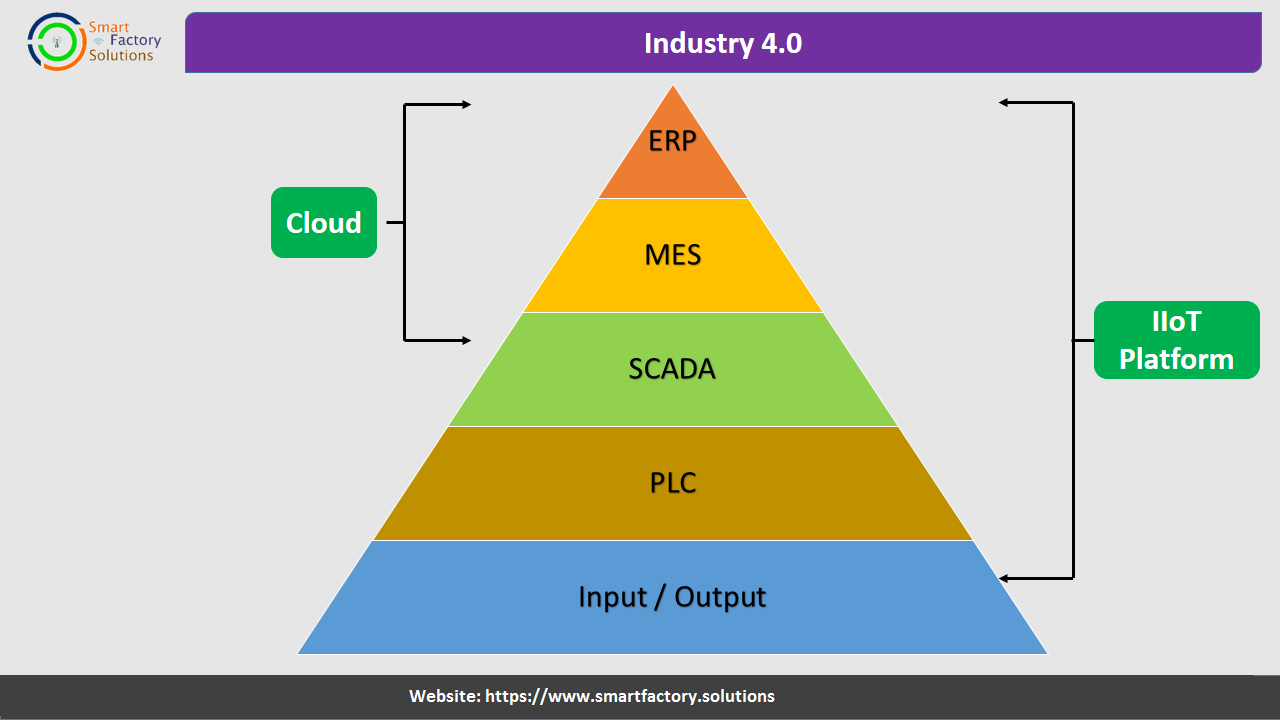
IIot platform which includes various software , hardware and it's connected with each other .
The major component of industry 4.0 is ERP, PLC, Input / Output Devices and SCADA.
SCADA system connected with ERP & MES.
Industry 4.0
Enterprise Resource Planning
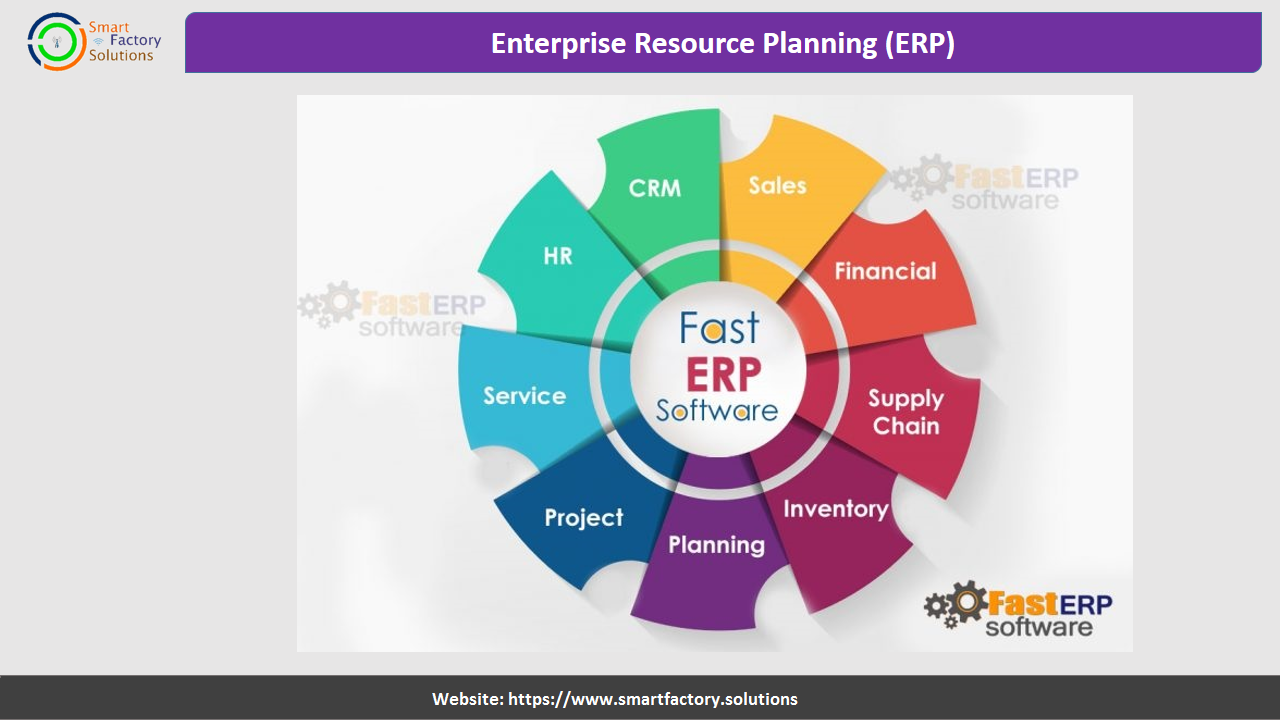
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning and refers to software designed to plan and manage all the resources like Men, Material, Machine, Money, Space,Information etc for all types of business functions like Sales, Bill of Materials, Process Planning, Material Planning, Production, Purchase, Inventory, Quality, Maintenance, Finance, Human resources etc.
Today, ERP has expanded to encompass business intelligence (BI) while also handling "front-office" functions such as sales force automation (SFA), marketing automation and ecommerce.
ERP software is a tool that centralizes a company’s database of information, automates routine tasks and simplifies business processes.
Benefits of ERP :
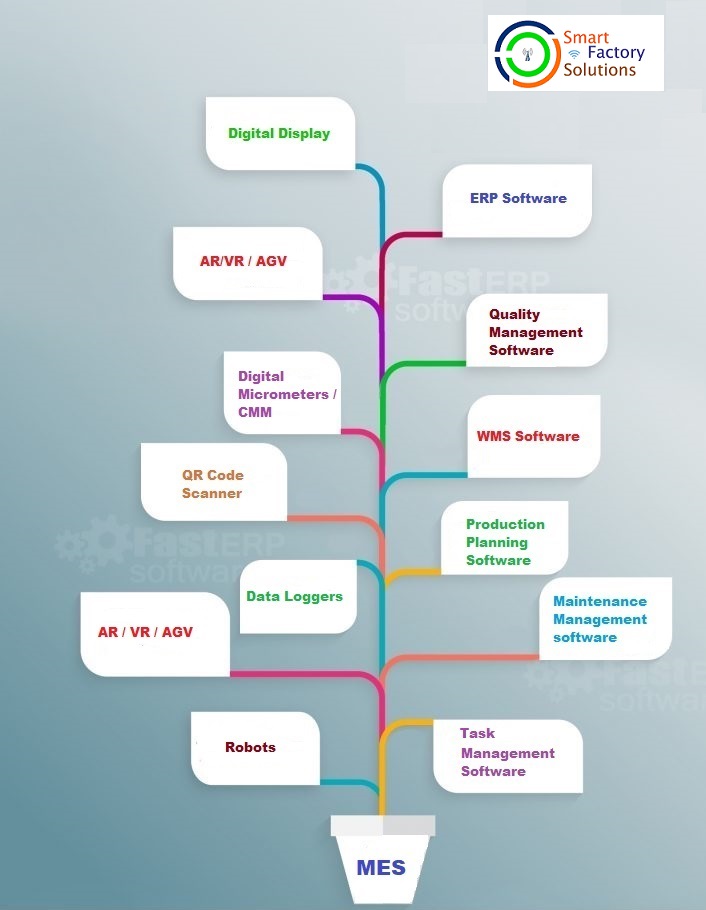
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is integrated software solution which integrates enterprise software systems in realtime with manufacturing machines, processes, manpower, equipments, instruments, storage systems together with Information capturing, processing and displaying relevant information for monitoring and control of inputs.processes and outputs to achieve targeted planned standards of input and output in manufacturing lifecycle.
MES software comes with tools for Production monitoring and managing activities across the various manufacturing processes:
Digital Product documentation
Product traceability with digital tools
Resource management
Automated Data collection and Display
People management
Benefits of Manufacturing Execution Systems:
Manufacturing Execution System
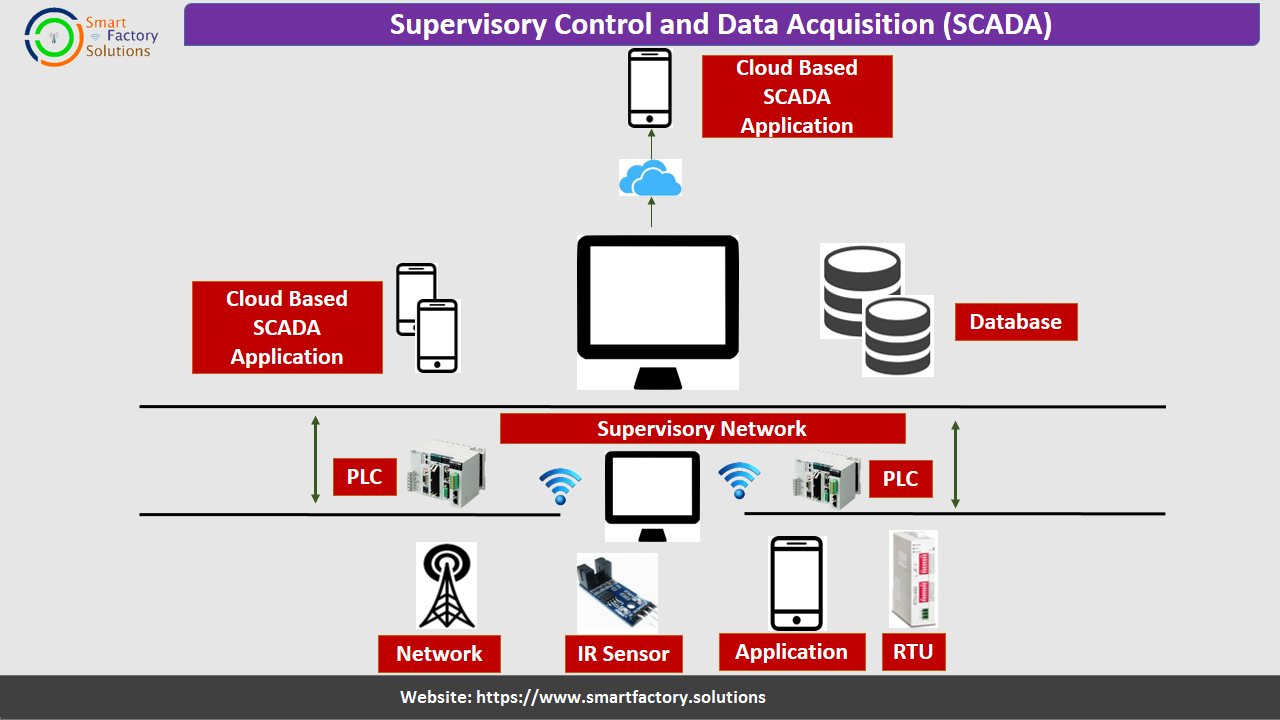
SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces (GUI) for high-level process supervisory management, while also comprising other peripheral devices like programmable logic controllers (PLC) and discrete proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers to interface with process plant or machinery.
The key attribute of a SCADA system is its ability to perform a supervisory operation over a variety of other proprietary devices.
SCADA is a type of process control system architecture that uses computers, networked data communications and graphical Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) to enable a high-level process supervisory management and control. SCADA systems communicate with other devices such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and PID controllers to interact with industrial process plant and equipment.
SCADA systems are used to control and monitor physical processes.
the example of scada is transmission of electricity, transportation of gas and oil in pipelines, water distribution, traffic lights, and other systems used as the basis of modern society.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC):
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) are defined as very small industrial computers that contain hardware and software used to perform control functions.
More specifically, a PLC would be used for the automation of industrial electromechanical processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines and food processing.
They are designed for multiple arrangements of digital and analog inputs and outputs with extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact.
A PLC will consist of two basic sections: the central processing unit (CPU) and the Input/Output (I/O) interface system.
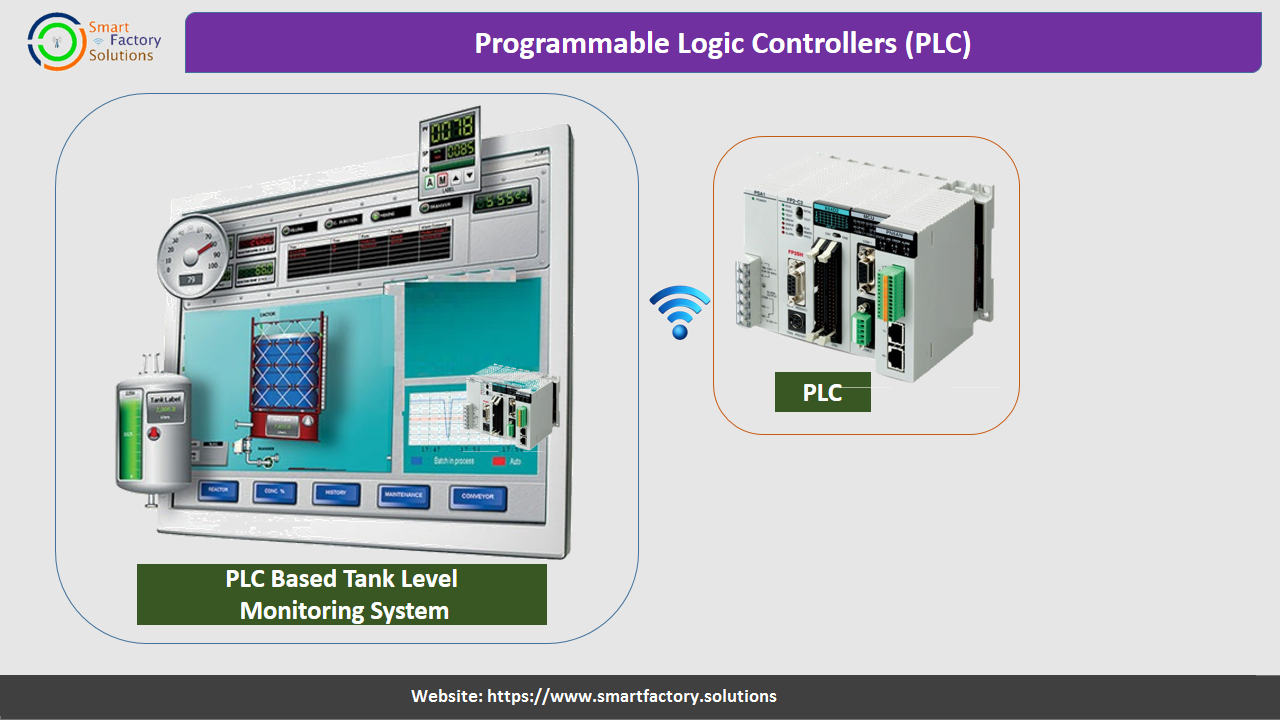
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
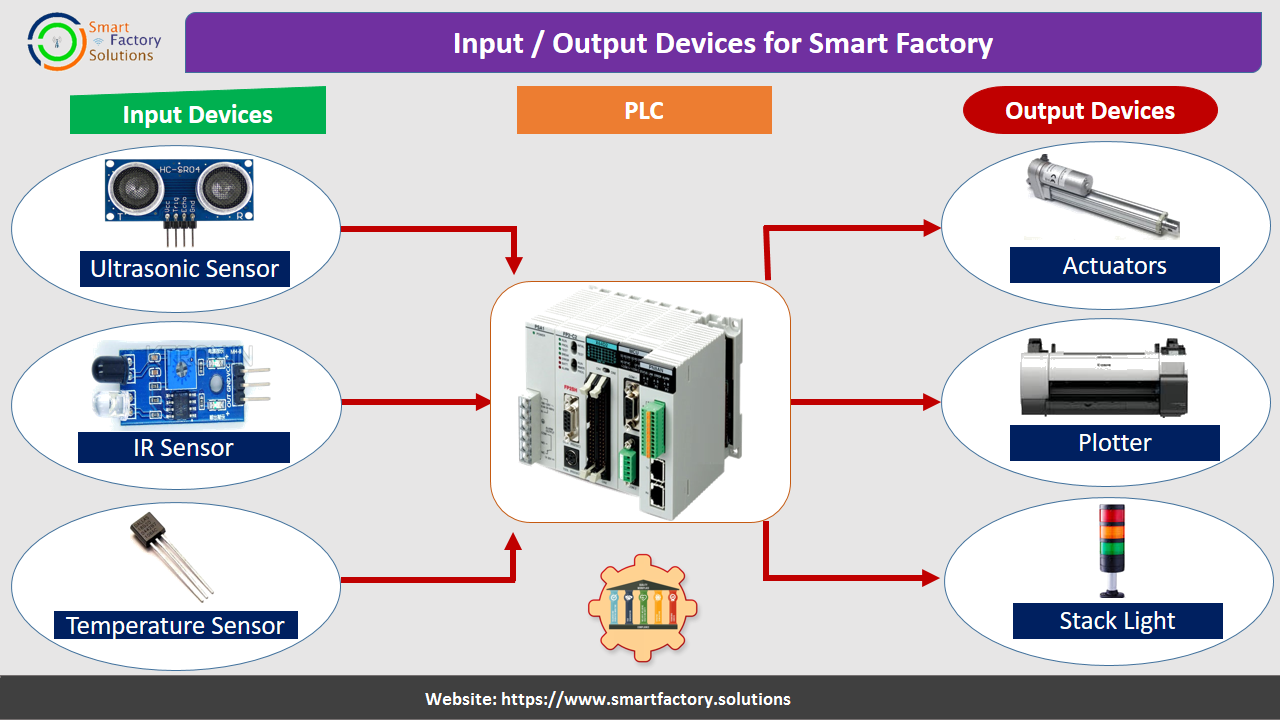
Input / Output Devices
Industrial IoT, are systems developed for investigating the status of any components of Smart Factory like Smart Machine,Product,Process,People etc. The presence of real-time data enables to make resources highly efficient. Furthermore, each machine is a part of connected as a Work centers. There is connectivity from machine to machine and therefore ability for any one operator to see a effect of line balancing on flow of the production line accordingly.
IIOT is a bridge between the shop floor and the management level that needed to make operational and scheduling decisions, based on efficiency and product results. It provides key input of machine monitoring to production planning software,Quality management software as well as machine maintenance software to provide the Business Analytics based on real time actual data.
IIOT is a bridge between the shop floor and the management level that needed to make operational and scheduling decisions, based on efficiency and product results. It provides key input of machine monitoring to production planning software,Quality management software as well as machine maintenance software to provide the Business Analytics based on real time actual data.
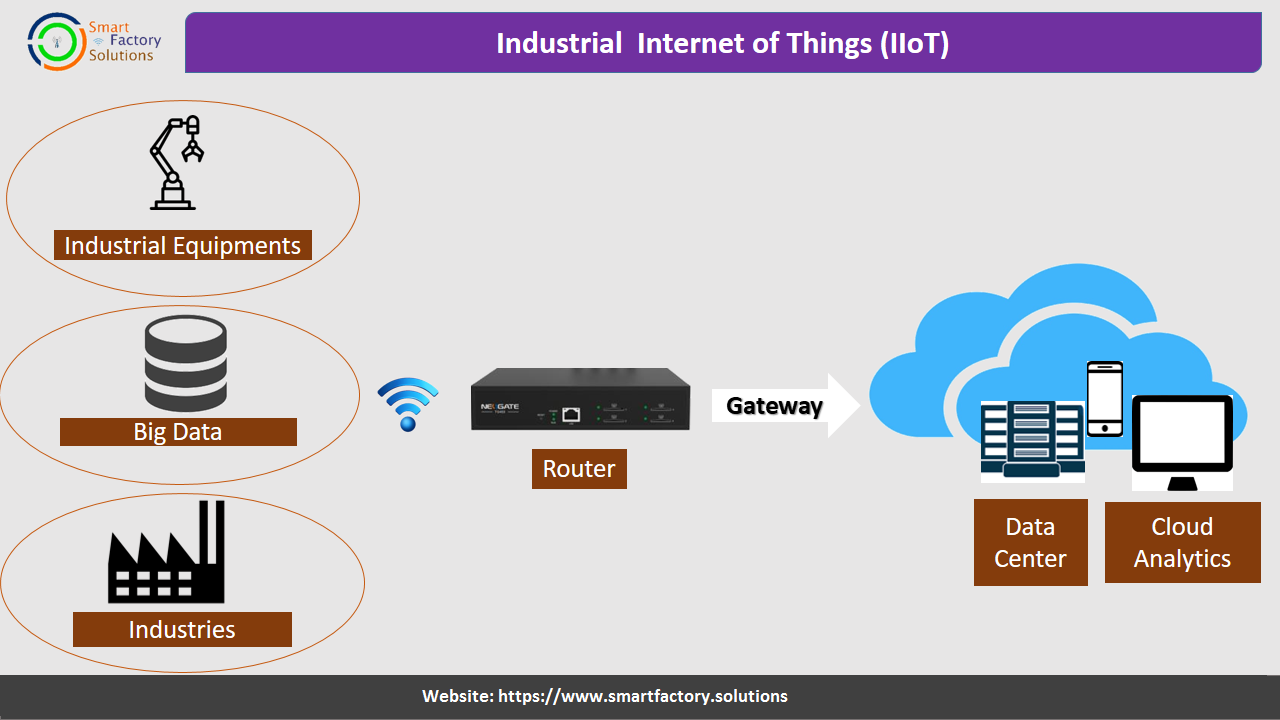
Industrial IoT
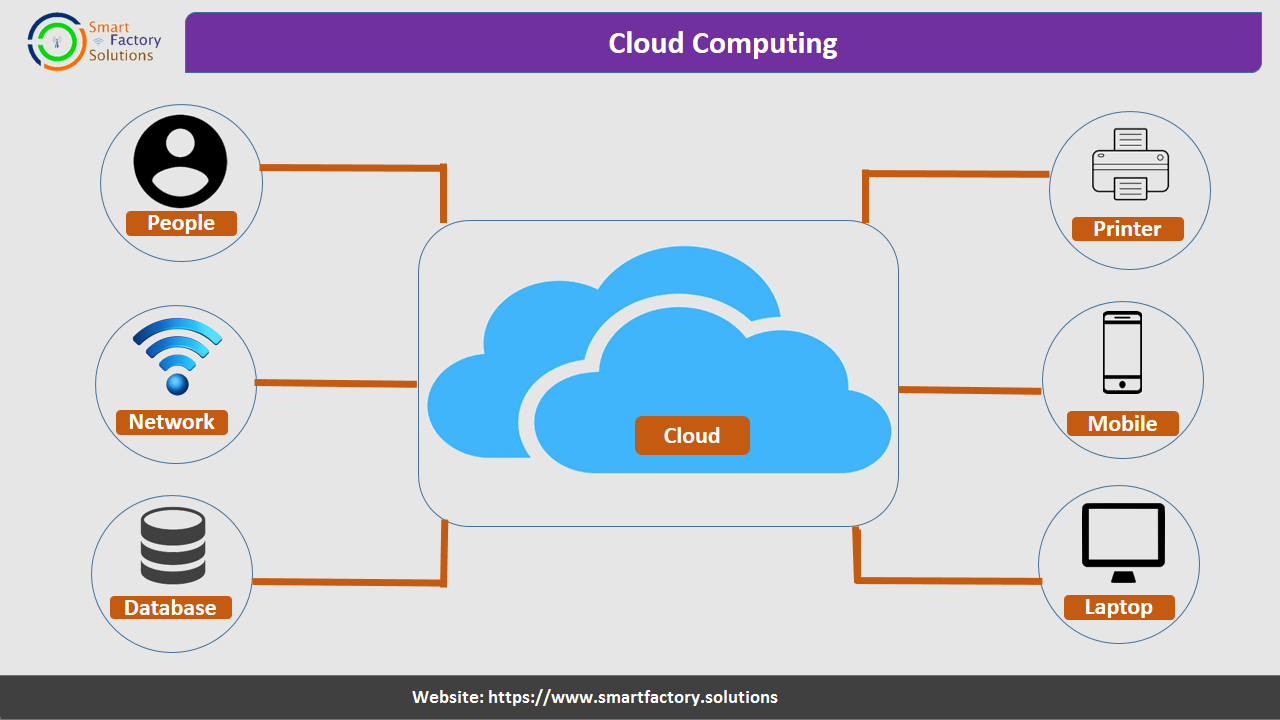
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You typically pay only for cloud services you use, helping lower your operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently and scale as your business needs change.
Cloud computing is an application-based software infrastructure that stores data on remote serves, which can be accessed through the internet.The front end enables a user to access data stored in the cloud using an internet browser or a cloud computing software.
Cloud computing offers businesses with scalable computing resources hence saving them on the cost of acquiring and maintaining them.
Edge computing is a distributed computing framework which brings computation and data storage closer to the source of the data, thus improving response time and saving bandwidth.
With edge computing, less data needs to be transmitted to the cloud. This is particularly useful for collecting high-frequency data that is used to run machine learning algorithms. Since this data can be processed at the edge, it can be acted on immediately. In contrast, if this high-frequency data was to be transmitted to the cloud, processed, and then acted on, there would be a latency effect. Edge computing solves this problem.
In Edge Computing Edge devices are equipment that manage the flow of data between a local network and the cloud. They act as a gateway between connected equipment on a local network and the software platform that is used to analyze the data.
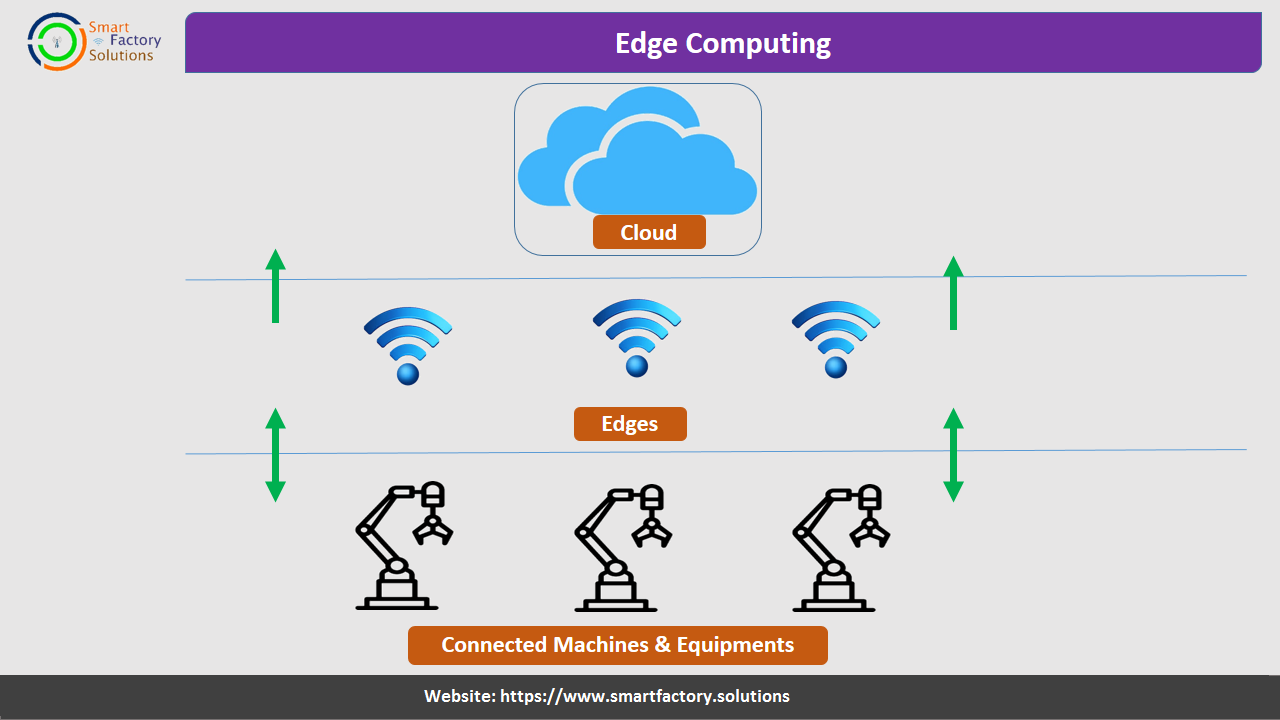
Edge Computing
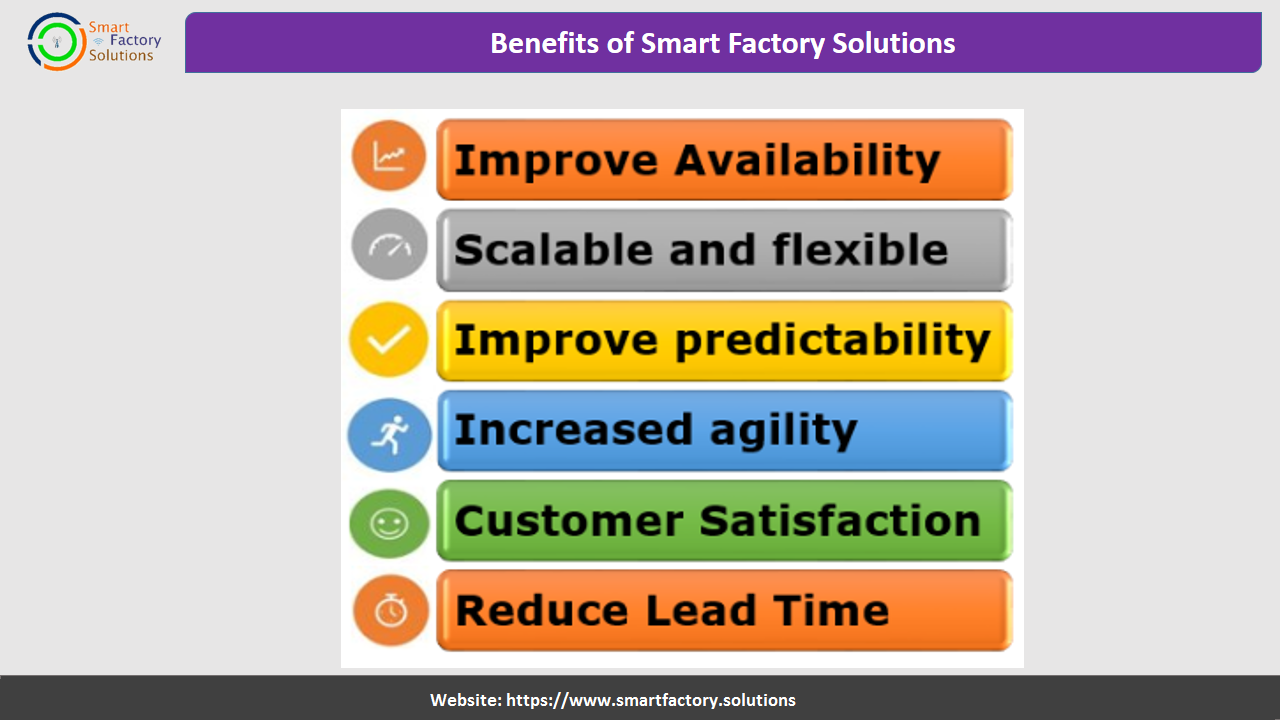
Benefits of Smart Factory Solutions
Improved Productivity :
Smart manufacturing processes provide greater access to data across an entire supply chain network.
Innovation and Higher Quality Products:
Smart manufacturing data shows where customer needs are and managers can find opportunities for new products or re-imagined products of a higher quality.
Maximum flexibility:
Smart Factory systems are engineered to suit different manufacturing environments and production setups. This ensures maximum operation flexibility.
Scalable and flexible :
Easy to customize and make changes in the future.
Improved predictability:
Infinite Uptime’s IDE (Industrial Data Enabler) calculates mechanical data through edge computing to deliver predictive maintenance.
Increased agility :
Using advance embedded sensors technology, Smart Factory systems automatically recognize manufacturing demands. This will allow supply chain to respond with better agility.
Continuously pull traditional datasets along with new sensor and location based Databases.
Real-time-data enabling collaboration with supplier and customer.
Collaboration across departments(feedback from production to product developement).
Reliable,predictable production capacity.
Increased asset uptime and production efficiency.
lightly automation production and material handling with minimal human interaction.
Live materials and tools to support quick and consistant decision making.
Real time linkages to customer demand forecasts.
Transparent customer order tracking.
Predictive enomaly identification and resolution.
Automated restocking and replenishment/
Early identification of supplier quality issues.
Real-time safety monitoring.
Flexible and adaptable scheduling and chaneover.
Implementation and product changes to see imapact in real-time.
Configuration factory layout and equipments.